Risk mitigation in AI systems uses autonomous agents to detect, assess, and reduce enterprise threats.
Risk mitigation refers to the process of identifying, assessing, and controlling potential threats to an organization’s operations, data, or strategy. It focuses on reducing risk exposure and ensuring effective risk management across cybersecurity, compliance, and operational domains. In agentic AI platforms, mitigation is handled through specialized agents that autonomously assess, prioritize, and respond to risk events across operational domains.
Detailed Definition & Explanation
Risk mitigation is a core component of the broader risk management process. It involves developing and implementing strategies to reduce the likelihood and impact of potential risks, whether they stem from cybersecurity breaches, operational failures, financial volatility, or strategic misalignment. Risk mitigation focuses on proactive planning, continuous monitoring, and control measures designed to minimize risks before they materialize as risk events.
The goal of risk mitigation is not to eliminate all risks but to prioritize and manage them in a way that aligns with the organization’s tolerance levels and business objectives. Effective risk mitigation strategies often involve multiple layers of controls, from technological safeguards to policy adjustments and incident response planning. These strategies may include everything from improving data security protocols and implementing access controls to diversifying suppliers and automating regulatory compliance workflows.
In enterprise settings, risk mitigation tools are increasingly AI-driven and data-powered, supporting real-time risk identification, dynamic risk assessment, and continuous tracking of business risks. These systems are essential in environments where the risk landscape is constantly evolving and where minimizing risks has become a competitive advantage.
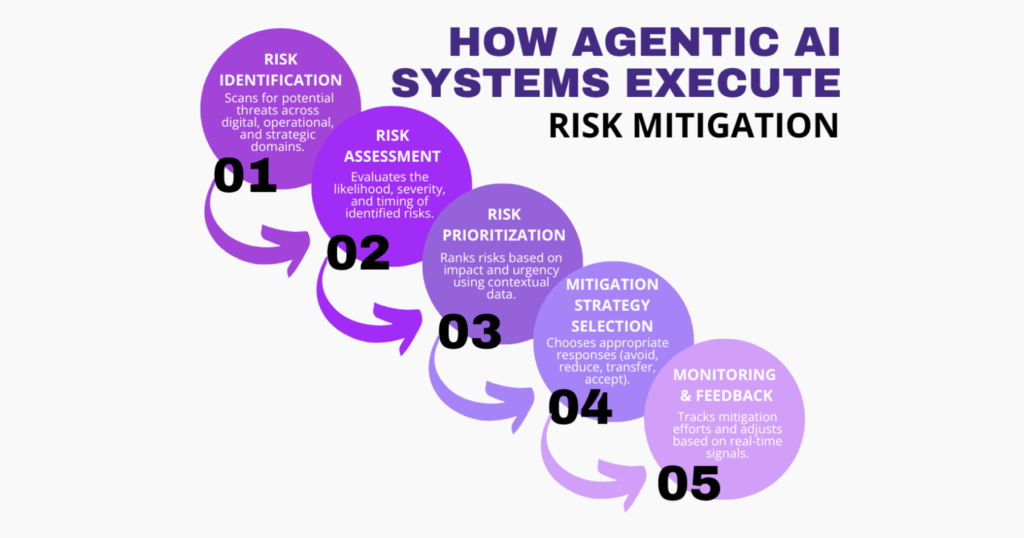
Why It Matters
Reduces enterprise exposure to cybersecurity threats and data breaches
Effective risk mitigation strengthens data security by embedding threat detection, encryption, and access controls into enterprise systems. In financial services, real time monitoring agents detect anomalies in transactions or API usage, reducing the chance of a data breach. In higher education, mitigation workflows include proactive controls around student records and identity management.
Improves operational continuity and decision-making in dynamic environments
By identifying and minimizing risks early, organizations can maintain service levels during disruptions. In e-commerce, risk mitigation agents predict inventory bottlenecks or third-party delays, enabling contingency planning. In insurance, operational risks are flagged through agentic assessments before claim backlogs or compliance violations emerge.
Supports regulatory compliance and informed risk management strategies
AI-enabled systems can continuously evaluate controls and help align with changing regulatory requirements. In consumer products, agents monitor for policy breaches in supply chain documentation. In financial services, enterprise risk management frameworks integrate with audit trails and policy engines to ensure oversight and compliance.
Enables proactive strategic risk mitigation in evolving markets
Strategic risk, such as entering new markets or launching AI products, requires scenario planning and adaptive risk reduction. In CPS, risk mitigation includes evaluating supplier diversification or geopolitical exposure. In higher education, strategic risks like enrollment shifts are managed via forecasting tools and automated intervention workflows.
Drives long-term resilience through continuous improvement and feedback loops
Modern risk mitigation systems are data-driven and self-improving. In insurance, feedback from rejected claims helps update risk models. In e-commerce, AI agents analyze post-incident outcomes to adjust inventory and shipping logic. These continuous learning loops support effective risk management in volatile business environments.
Adoption Trends and Real-World Examples
Risk mitigation is becoming a strategic imperative across sectors as organizations face growing operational complexity, cyber threats, and compliance demands. According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023, the global average cost of a data breach touched $4.45 million in 2023, indicating an all-time high for the report. Moreover, organizations with mature risk management processes and AI-driven detection systems cut breach costs by over $1.7 million compared to those without.
In light of such data, enterprises are actively investing in enterprise risk management frameworks that combine real-time monitoring, analytics, and automated controls.
FD Ryze: FD Ryze deploys intelligent risk mitigation agents that monitor operational risks, flag compliance gaps, and trigger real-time controls across industries. The platform integrates with existing systems to embed risk reduction into every business function.
ServiceNow Risk Management: ServiceNow’s integrated risk platform includes AI-powered agents that automate the process of identifying, assessing, and controlling business risks. It enables users to align mitigation workflows with enterprise goals and regulatory frameworks, particularly in IT, finance, and HR operations.
LogicGate Risk Cloud: LogicGate’s no-code GRC platform enables enterprises to design and execute mitigation workflows tailored to operational and strategic risk. It supports automated alerts, customizable assessments, and detailed audit trails that simplify continuous monitoring and risk prioritization.
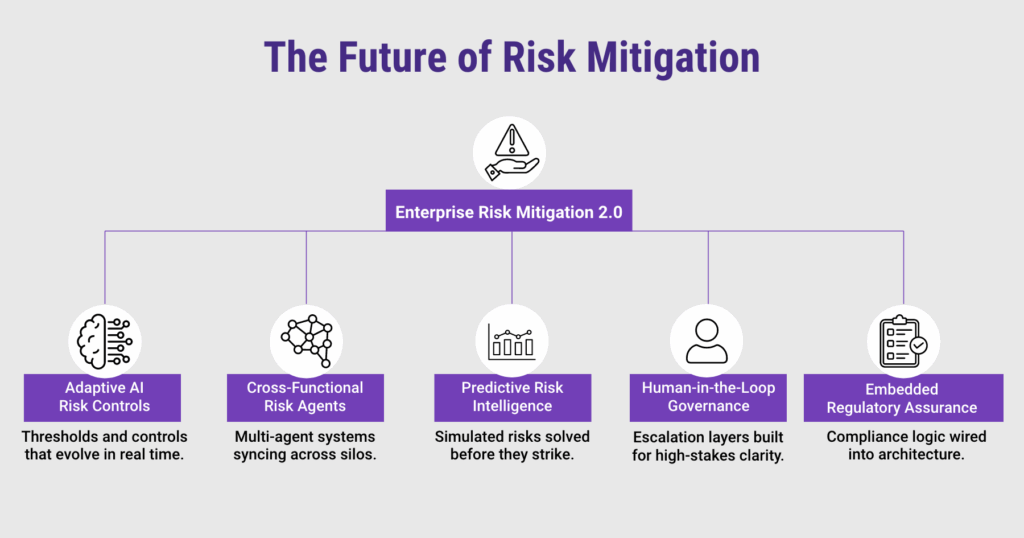
Risk mitigation will shift from static controls to adaptive, AI-driven systems
Next-gen systems will automatically adjust thresholds, policies, and escalation paths based on new threat intelligence. Enterprises must invest in AI models that learn from risk events and embed them into control systems for adaptive response.
Cross-functional mitigation will become the norm in enterprise risk management
As operational, cybersecurity, and strategic risks converge, organizations will use multi-agent frameworks that orchestrate responses across departments. Companies must create centralized governance layers and shared data taxonomies to enable this level of coordination.
Proactive risk intelligence will drive mitigation before impact occurs
Predictive analytics and simulation agents will forecast potential threats and recommend interventions. In industries like insurance and finance, risk modeling will shift from retroactive to forward-looking, requiring data lakes and simulation-ready infrastructure.
Human-in-the-loop escalation will remain critical in high-stakes scenarios
Despite automation, certain decisions—especially those related to strategic risk or customer-facing issues—will require human review. Organizations should build escalation workflows and audit trails that reinforce accountability without slowing response time.
Regulatory alignment will move from compliance checklists to embedded assurance
Risk mitigation strategies will include embedded compliance logic in core systems, ensuring that every AI decision is both auditable and policy-aligned. Enterprises must adopt governance-as-code models to integrate controls at the system architecture level.
Related Terms
- Risk Assessment
- Risk-Based Orchestration
- Enterprise Risk Management
- Operational Risks
- Strategic Risk
- Compliance Automation
- Cybersecurity Threats
- Data Breach Prevention
- Business Continuity
- Control Systems
