Orchestration refers to automated coordination of tasks, systems, data, and agents to deliver seamless process flows.
Orchestration refers to the automated coordination of tasks, systems, data, and agents across an enterprise to achieve a specific outcome. In AI and Agentic AI environments, orchestration ensures that workflows adapt dynamically, decisions stay context-aware, and processes are executed seamlessly from end to end.
Detailed Definition & Explanation
Orchestration in AI is the process of managing how various components—data flows, tasks, APIs, systems, and agents—work together in harmony to achieve a business goal. Unlike simple automation, which executes isolated tasks, orchestration enables coordinated, multi-step workflows that are dynamic, adaptable, and contextually intelligent.
In the context of Agentic AI, orchestration includes both workflow orchestration (sequencing tasks across departments or systems) and agent orchestration (enabling micro-agents to collaborate, delegate, and self-organize around goals).
Orchestration often involves:
- Task scheduling and dependency resolution
- Data routing across systems
- Trigger-based decision-making
- Role-based agent activation
- Real-time adjustments based on outcome feedback
Modern orchestration platforms use AI and APIs to bridge silos, connect structured and unstructured data sources, and trigger adaptive workflows across cloud, on-premise, and hybrid environments.
Types of Orchestration in Agentic AI
Workflow Orchestration: Coordinating multi-step processes like claims adjudication, order fulfillment, or onboarding.
This typically involves defining task sequences via low-code orchestration engines or DSLs (domain-specific languages), where each task is conditionally triggered by events, status updates, or external API calls. Agentic AI systems enhance this by enabling agents to monitor state, adjust routing logic, and re-prioritize steps dynamically.
Process Orchestration: Managing dependencies, approvals, and dynamic routing within enterprise business logic.
This is achieved through business process management (BPM) tools or event-driven architectures where agents manage stateful transitions, enforce policies, and invoke sub-processes via RESTful or message-based communication. Conditional branching, SLA timers, and role-based approvals are embedded directly into process graphs.
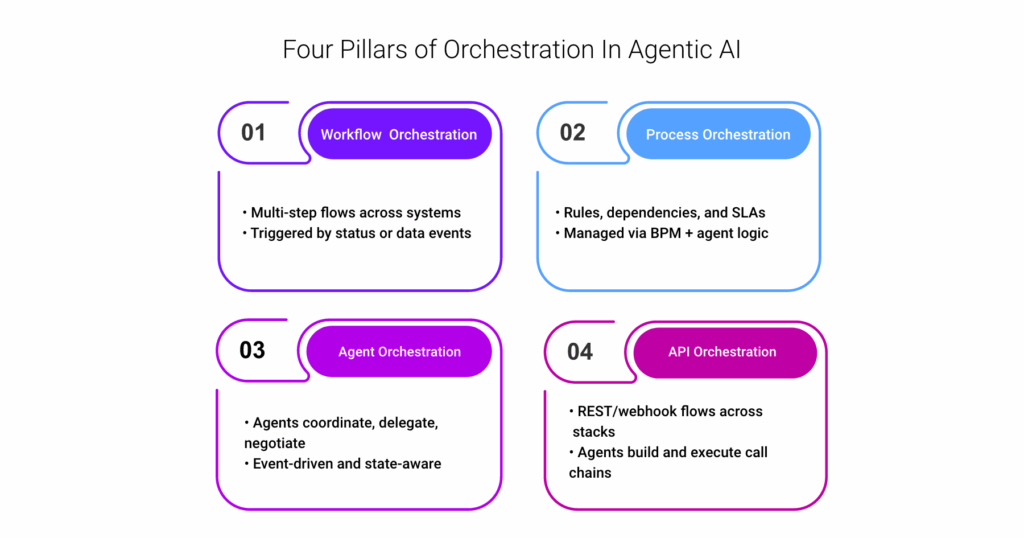
Agent Orchestration: Deploying and synchronizing autonomous agents that act on specific triggers or shared goals.
Agents register themselves within an orchestration layer, subscribe to relevant signals (e.g., Kafka topics, API events), and negotiate task ownership via coordination protocols or shared memory/state models. Some use task queues or token-based activation models to avoid duplication or conflict.
API Orchestration: Integrating services and systems in real time, often across legacy and cloud-native environments.
Here, orchestration flows rely on REST APIs, webhooks, and JSON payloads to sequence actions between microservices and external systems. Agentic AI enhances this by letting agents dynamically compose API calls based on context, chaining endpoints, validating responses, and retrying failed steps autonomously.
Why It Matters
Unlocks End-to-End Autonomy
Orchestration transforms disconnected tasks into intelligent, goal-aligned workflows, emerging as the backbone of agentic execution. In financial services, for example, this enables agents to automate client onboarding from KYC to credit checks, without human handoffs or system delays.
Eliminates Bottlenecks and Silos
Enterprise-wide orchestration bridges departments, tools, and data, making it easier to respond in real time. In an industry like ecommerce, agents can orchestrate everything from inventory restocking to cart abandonment follow-ups, reducing lag between marketing, logistics, and support.
Supports AI Governance and Control
With structured orchestration, organizations can enforce business rules, compliance boundaries, and audit trails, even across autonomous agents. For instance, in insurance, this ensures that claims-handling agents respect jurisdiction-specific regulations while still resolving cases with speed and autonomy.
Accelerates Time to Value
Instead of building bespoke flows, orchestration platforms deliver reusable logic that adapts to different use cases. In higher education, for instance, course recommendation agents can be orchestrated with enrollment, scheduling, and advising systems, without rebuilding logic for each department.
Enables Scalable Agentic Systems
As micro-agents multiply, orchestration ensures they collaborate productively, avoid conflicts, and align with overarching objectives. In consumer products, this lets planning, procurement, and marketing agents coordinate promotions based on forecast shifts or supply chain disruptions without manual oversight.
Real-World Examples
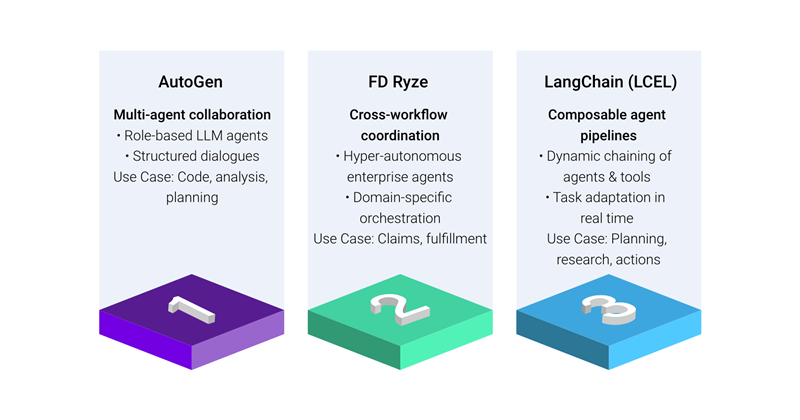
AutoGen
AutoGen enables agentic orchestration by coordinating multiple LLM-based agents with distinct roles that collaborate through structured dialogue, allowing goal-driven problem-solving in tasks like code generation, data analysis, and multi-step reasoning.
FD Ryze
FD Ryze enables agentic orchestration across systems and workflows, allowing autonomous agents to coordinate tasks like insurance claims processing or e-commerce order fulfillment with real-time context and precision.
LangChain Expression Language (LCEL)
LCEL powers agentic orchestration by chaining autonomous agents, tools, and prompts into adaptive workflows, enabling dynamic task delegation and decision-making across use cases like research synthesis, planning, and tool-based execution.
What Lies Ahead
Agent-Orchestrated Enterprises
Orchestration will shift from centralized control to agent-led coordination, where micro-agents initiate and manage their own workflows.
Semantic and Goal-Based Orchestration
Instead of hardcoded rules, future orchestration layers will interpret business intent from natural language prompts or goals.
Cross-Layer Integration
Orchestration will span not just software layers but physical + digital + human environments (e.g., IoT + ERP + Agentic AI).
Autonomic Orchestration
Systems will monitor their own performance and adjust orchestration logic on the fly based on context, constraints, or drift.
Orchestration as a Strategic Layer
It will evolve from a backend function to a core pillar of enterprise intelligence, driving real-time adaptation and resilience.
Related Terms
- Workflow Automation
- Multi-Agent Systems
- Hyperautomation
- Autonomous Agents
- Decision Intelligence
- Process Intelligence
- API Integration
- AI Governance
- Event-Driven Architecture
- Agentic AI
