Intelligent automation empowers agents to learn, adapt, and act across digital systems.
Intelligent automation refers to the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and robotic process automation (RPA) to create self-improving systems that handle complex workflows with minimal human input. In Agentic AI environments, autonomous agents leverage intelligent automation to perceive context, make decisions, and initiate actions across systems and processes.
Detailed Definition & Explanation
Unlike traditional automation, which relies on rigid scripts, intelligent automation combines AI, machine learning, natural language processing, and decision logic to handle dynamic, unstructured tasks. Intelligent automation systems not only execute instructions but can also interpret data, learn from outcomes, and optimize actions over time.
In Agentic AI architectures, intelligent automation is the execution engine behind self-directed agents. These agents are capable of:
- Ingesting inputs from structured and unstructured sources (e.g., databases, emails, chat logs)
- Understanding context using NLP, LLMs, or pretrained classification models
- Making decisions based on business rules, real-time insights, and policy constraints
- Taking action via RPA bots, APIs, and orchestration platforms to fulfill objectives
Example workflows include onboarding employees, processing insurance claims, managing IT tickets, or personalizing e-commerce experiences, all autonomously handled by agent-driven intelligent automation.
Why It Matters
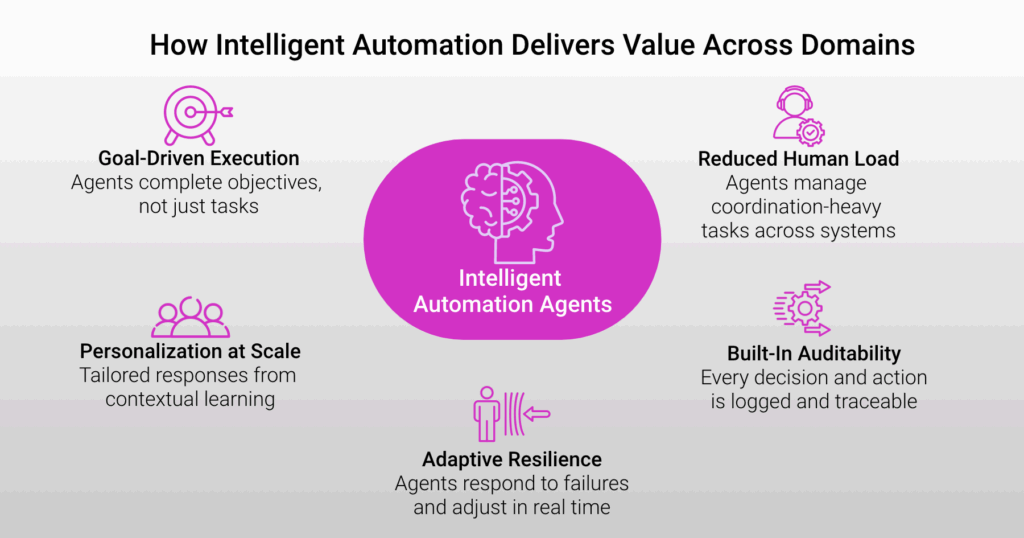
Enables Goal-Driven Process Execution
Agents automate not just tasks, but entire objectives, making decisions based on defined outcomes and adapting pathways based on real-time data. In financial services, agents can manage loan processing by checking credit, assessing risk, and generating approvals autonomously. In ecommerce, intelligent agents can handle post-purchase journeys, managing fulfillment updates, returns, and loyalty rewards.
Reduces Operational Load on Human Teams
By handling multi-step tasks across systems (APIs, databases, CRM), intelligent automation reduces the need for manual coordination. In insurance, agents can auto-validate policyholder data, check claim histories, and pre-fill forms for underwriters. In CPS, it helps coordinate logistics by syncing inventory, packaging, and delivery based on live inputs.
Enhances Personalization at Scale
Agents learn from contextual data and adjust outputs for each user, enabling custom communication, recommendations, and workflows. In higher education, agents can personalize course plans or financial aid recommendations based on student history and preferences. In retail, marketing agents tailor campaigns based on real-time behavior and purchase patterns.
Increases Process Resilience and Adaptability
By embedding decision logic and adaptive behaviors into workflows, agents can continue functioning during disruptions or changes. In insurance, if a primary APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) is unavailable, agents reroute claims through alternate data sources. In banking, agents can switch KYC methods or verification paths depending on user channel or geography.
Improves Auditability and Compliance
Intelligent automation systems track every step taken, maintaining logs and rationale for actions taken. In financial services, this ensures audit trails for transaction approval flows. In education, it tracks student communications, support interactions, and eligibility decisions for transparency.
Real-World Examples
UiPath + OpenAI (2024)
UiPath integrates with OpenAI’s GPT models to power intelligent document processing, summarization, and policy interpretation in automation workflows. It enables context-aware robotic process automation (RPA) that can act on unstructured text.
ServiceNow’s Generative AI Automation Layer
ServiceNow uses GenAI and intelligent automation to help enterprises automate IT service requests, HR cases, and compliance reviews. The Now Assist platform combines workflow logic with LLMs to dynamically handle and route requests.
FD Ryze
FD Ryze embeds intelligent automation through autonomous micro-agents that manage high-volume workflows in domains like insurance claims, e-commerce fulfillment, and risk assessment. These agents reason through events, coordinate across APIs, and trigger downstream actions without static rule chains.
What Lies Ahead
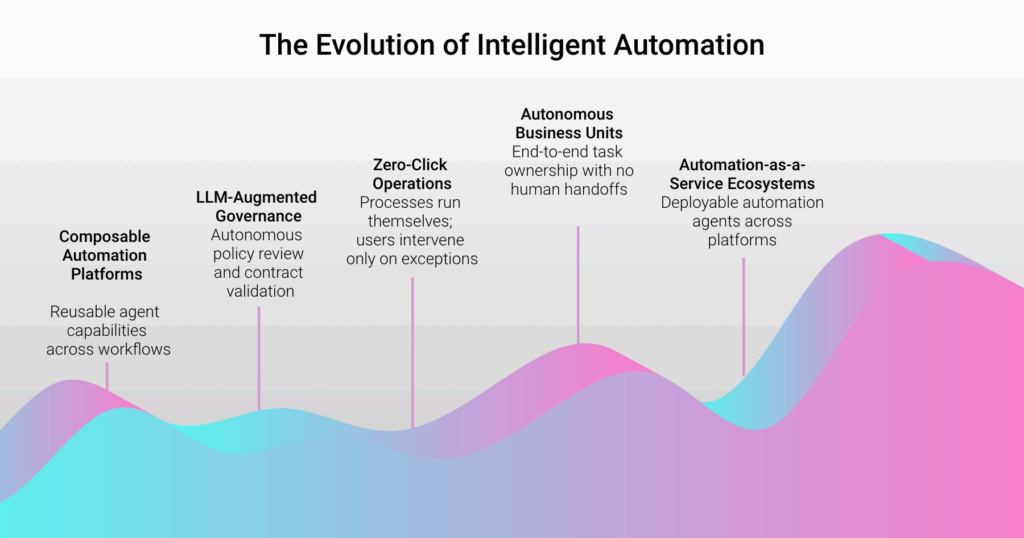
- Autonomous Business Units
Departments will increasingly function as AI-driven units, where agents execute end-to-end tasks—from intake to outcome—without handoffs.
- Composable Automation Platforms
Enterprises will build modular agent ecosystems where functions (e.g., document classification, policy validation) are shared, reused, and adapted across workflows.
- Zero-Click Operations
Back-office systems will shift to predictive, agent-led execution, where no user input is needed unless exceptions arise.
- LLM-Augmented Governance
Agents will auto-review policies, redline contracts, or validate controls using LLMs combined with policy insight agents.
- Automation-as-a-Service Ecosystems
Vendors will offer “plug-and-play” intelligent automation agents deployable across SaaS platforms, making it easier for enterprises to adopt automation incrementally.
Related Terms
- Business Process Automation
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
- Cognitive Automation
- Intelligent Document Processing
